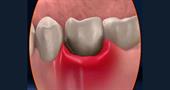
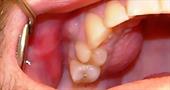
The most common and most common lesion of the oral mucosa is stomatitis. The disease is difficult to determine due to the fact that there are no special tests for diagnosis, and in terms of its symptoms, stomatitis is similar to many other diseases of the oral cavity. Stomatitis can appear on the tongue, on the lips, or on the palatal surface. Depending on the named places of damage, the types of this disease are also distinguished: cheilitis, glossitis and palatinitis. With edema, keratinization of tissues and their peeling, the mucosal disease is called leukoplakia.
Causes
Inflammation of the oral mucosa can occur for a variety of reasons. The development of stomatitis, in particular, can be influenced by foreign and pathogenic microorganisms. In fact, there are many more reasons, and the mechanism of the onset of the disease is not fully understood. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, allergies, trauma to the mucosa with any objects or products, metabolic disorders - these are just some of the reasons under the influence of which stomatitis may appear.
Dental procedures, not necessarily associated with dental treatment, often provoke the appearance of stomatitis. A change in the chemical balance in the mouth or the reaction of the body to dentures, even brushing your teeth with a new toothpaste that traumatizes the mucous membrane or brought foreign substances - all this can cause inflammation.
Symptoms of an inflammatory disease
A variety of stomatitis plays a decisive role in the classification of various types of diseases of the oral mucosa. Failure to comply with oral hygiene leads to catarrhal stomatitis - a very common type of disease. Swelling of the mucous membrane, pain, redness are likely signs of catarrhal stomatitis , resulting from gastritis or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon or duodenum. Another reason for the development of stomatitis can be helminths. Often, a light coating of different colors may appear in the mouth, the smell becomes unpleasant, blood comes out of the gums.
The ulcerative type does not always develop as an independent disease , often such a disease is the result of complications after catarrhal stomatitis.
Small oval or round white sores that appear on the mucous membrane indicate infection with aphthous stomatitis. Ulcers can be located on the inside of the lower or upper lip, as well as on the buccal mucosa. Aphthous stomatitis often develops in children as an independent disease. But usually it occurs due to gastrointestinal diseases, allergic reactions, viral infections or rheumatism. Along with the characteristic manifestations, the inflammatory process may be accompanied by fever, swollen lymph nodes under the lower jaw, and pain when eating. Healing sores pass without a trace and do not leave any scars.
A chronic disease of the oral mucosa is called leukoplakia . The disease is characterized by lesions of the mucosa in the form of keratinization of the surfaces. It can develop on the membranes of the cheeks, at the mouth, on the lower lip. In rare cases, manifestations can be located in various parts of the tongue and in the region of the bottom of the oral surface. Among the causes that affect the occurrence of leukoplakia include injuries or cuts of the mucous membrane, burns from food. Gastrointestinal diseases are also considered one of the causes of this disease. The disease passes without discomfort or obvious symptoms. Sometimes there is itching or burning, which goes away on its own. The disease needs urgent treatment, otherwise it can develop into a malignant form. A trip to the doctor when signs of leukoplakia appear is mandatory.
Treatment
The main treatment of stomatitis is aimed at determining and eliminating the causes of its development. The inflammatory process is only a consequence, and after the removal of the stimulus, the development of the disease quickly stops. Sometimes stomatitis goes away on its own without treatment. But this is in rare cases, and you should not hope for it. At the slightest sign of illness, it is better to go to an appointment with a general practitioner or an experienced dentist. He will be able to determine the type of stomatitis and methods of treatment.
With a fungal disease, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy and drugs. Ordinary honey has a good disinfecting effect, and sea buckthorn oil can be used to heal wounds. You can rinse your mouth with antimicrobial tinctures and remedies. It is better not to use alcohol preparations. Decoctions based on medicinal plants help well. If the cause of the disease is in dentures, stones, or the consequences of treatment, it is better to remove foreign objects and treat them with a dentist.
Improper treatment or lack of it can lead to serious complications.