The formation of bumps on the gums is a common phenomenon, and one of the gum diseases can be the cause. Moreover, the presence of a fistula or the so-called bumps indicates that the disease has entered a progressive stage. Most often, the cause of the appearance of a hard or purulent bump on the gum is insufficient oral hygiene, however, a fistula can have other causes. If you find any change in the oral cavity - bumps, seals, swelling, swelling - you should contact your dentist. The doctor, after establishing an accurate diagnosis, will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Causes of bumps on the gums
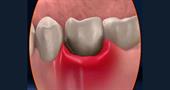
- Fistula . The fistulous outlet looks like a growth about 5 mm in diameter and 3 mm with a white tip on the surface (patients describe the problem as: white bump on the gum , bump with pus on the gum ). The fistula in its structure resembles a channel for the removal of purulent accumulations that form in the inflammatory focus deep under the skin. Inside the gums there is a focus of infection, and the formation of a fistula indicates its growth. Despite the fact that pus is regularly excreted from the body and does not accumulate inside, inflammation can become chronic if timely treatment is not started.
In order to get rid of pain and help the body remove purulent accumulations, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with a soda solution. In a glass of hot water - half a teaspoon of salt and soda. It is recommended to rinse your mouth every 1.5 hours daily. Until the lump is completely resorbed.
- Periodontitis . Most often it manifests itself in the form of a dense bump, about 1 cm in diameter (patients describe the problem as: a hard lump on the gum , a bump above the gum does not hurt ). The most common reason for the development of periodontitis is unfilled dental canals or pulpitis. The reproduction of bacteria leads to the formation of an abscess at the top of the root of the diseased tooth. If timely treatment is not carried out, a granuloma forms at this place, and then a cyst.
With a small inflammatory process, the infected tooth is subject to unsealing, cleaning of the canals and dental tissues affected by caries. In order for the pus to have an exit channel from the focus of infection, the root canals expand. After that, the wound is treated with antiseptic preparations and a course of antibiotic treatment is prescribed. A temporary filling is placed, which after a while is replaced with a permanent one.
- Periostitis . This is a complex course of periodontitis, when pus does not break out through the soft tissues of the gums, but into the bone, which leads to its inflammation. This disease is known as flux . Symptoms of periostitis, in addition to bumps on the gums, are fever, swelling of soft tissues, cheeks, lips, inflammation of the lymph nodes, and acute pain.
Removal of fillings or crowns, cleaning and expansion of channels. Medicine is placed under the temporary filling. After 2-3 months, the tooth cavity is re-washed with antiseptics and a new dose of medication is applied. The temporary filling is placed again. After another 2-3 months, the temporary filling is replaced by a permanent one.
With the development of a complication in the form of a cyst, the tooth, near the root of which the inflammatory process occurs, must be removed.
- Gingivitis . Inadequate oral hygiene leads to bleeding gums , slight swelling and the appearance of small red lesions. This is the initial stage of periodontitis (patients describe the problem as: a red bump on the gum ).
Treatment is carried out at home using special gels, ointments and rinse solutions. In order to prevent, it is necessary to maintain oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis . Inflamed gums cause loosening of the teeth , gaps, the so-called pockets, form between the tooth and the gum. These periodontal pockets become breeding grounds for bacteria and tartar. Advanced periodontitis leads to the accumulation of a large amount of pus between the tooth and gum, which causes the gums to become covered with whitish, bulging bumps.
The course of treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. At the first stage, the dentist removes dental deposits, after which the periodontal pockets are washed with antiseptic preparations. If the pocket is too deep, it becomes necessary to depulp the tooth. After a course of antibiotics, curettage of periodontal pockets is performed.
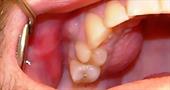
- Epulis . The popular name is "supergingival" (patients describe the problem as: a bump above the gum ). The cause of supragingival development is regular mechanical trauma to the gums. A poorly installed prosthesis, a convex filling, the edge of a sharp chipped tooth, regularly injuring the soft tissues of the gums, can lead to the appearance of a tumor or growth. The bump with epulis has an impressive size - up to 3 cm and a bluish tint.
Epulis capsules, in order to avoid re-development, are carefully scraped out. If necessary, the teeth located next to the focus of the disease and causing its formation, are subject to removal.
- Hematoma . When a tooth is removed, a watery soft swelling appears on the injured gum tissue - a hematoma (patients describe the problem as: a bump on the gum after tooth extraction ). Most often, it resolves after a few days and does not require treatment.
Lump on the gums of a child
- A white hard bump on the baby's gum is a sign that a milk tooth will erupt soon in this place. To alleviate the condition of the child, special children's gels can be rubbed into the swollen gum area: Kalgel, Dentinox, etc.
- A white lump near or behind a milk tooth. Most often occurs in preschool children during the changing period of teeth. The white bump is a permanent tooth that is trying to cut through the gum. If milk teeth are not in a hurry to fall out, it is worth visiting a dentist to prevent the development of malocclusion .
- The appearance of a purulent bump on the gums of a child requires an urgent visit to the dentist. If an abscess or fistula was formed as a result of a disease of a milk tooth, then it should be removed to avoid the spread of infection to the germ of a permanent tooth.
- If a purulent outgrowth or bump has formed in the area of the molar, then all measures will be aimed at preserving it. In these cases, the bumps are opened, washed with antibacterial drugs. If necessary, a course of oral antibiotics is prescribed.
Folk remedies
In order to achieve a positive effect as soon as possible, alternative methods can be added to the treatment:
- For example, Kalanchoe not only has an anti-inflammatory effect, but also remarkably strengthens enamel and is a natural antibacterial agent. Kalanchoe juice is recommended to be rubbed into the area of \u200b\u200bthe formation of a cone or to chew a leaf of this flower washed and peeled from the film.
- Herbal tinctures. Sage, chamomile, calendula also have a calming effect and relieve inflammation. Rinsing the mouth with a tincture of these herbs promotes the resorption of bumps and tumors on the soft tissues of the gums. To prepare a decoction, 4 tablespoons of medicinal herbs are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water. The decoction is ready for use in thirty minutes. The optimum temperature for rinsing is approximately 36 degrees.
- A mixture of honey and salt. Both of these components have a positive effect on the oral mucosa. Salt helps soften tissues and remove purulent accumulations, and honey has a calming and antiseptic effect. To prepare a medicinal mixture, mix 1 teaspoon of sea salt with two teaspoons of honey.
It should be remembered! Treatment with folk remedies contributes to a speedy recovery, but in no way can replace the therapeutic treatment prescribed by the doctor.




Great information in easy to understand language! The most important thing will be clear to a person without a medical education. From practice, I can add that very often patients confuse flux and fistulous tract. Here is a complete explanation. Still, many are very worried about the white bump on the gum during the period of bite change. I would like to give advice to parents that at this time it is necessary to strengthen control over the quality of oral hygiene of the child and visit the doctor more often for preventive examinations.
Answer