Ulcerative stomatitis is a serious pathology of the oral mucosa, accompanied by inflammation and swelling. A severe form of dental disease is called Vincent's stomatitis. It affects the tissues of the oral cavity, provokes the formation of deep ulcers.
In most cases, young children aged 6 months to 3 years suffer from this form of stomatitis. Against the background of poor ecology and a seasonal decrease in the protective functions of immunity, the disease also manifests itself in the adult population.
Causes
The ulcerative form of stomatitis is a completely unexplored phenomenon. Inflammation and ulceration are caused by spindle-shaped bacteria. In a small amount, they are found on the oral mucosa in any person. Harmful bacteria are located in carious cavities, gum grooves. Symptoms of the disease do not appear until their number increases to a maximum.
The main reason for the development of Vincennes stomatitis is a decrease in general immunity. Several factors influence the deterioration of protective functions:
- Viral diseases (influenza, pneumonia, acute respiratory infections and SARS);
- chronic diseases;
- Overwork and strong physical exertion;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Lack of vitamins, minerals and trace elements in the body (avitaminosis);
- Strong stress.
Ulcerative stomatitis is a complication in case of improper or neglected treatment of allergic and herpetic stomatitis .
Improper oral hygiene, mechanical and chemical injuries of the mucous membrane - sharp edges of teeth, braces, hot food can provoke diseases.
Ulcerative stomatitis is not transmitted through household contact.
Symptoms
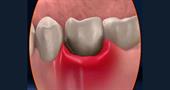
With a mild degree, the disease has common symptoms with ulcerative gingivitis - the upper part of the gum and the intergingival space become inflamed, swollen and redden, the patient experiences itching and burning, the mucous membranes dry out. When eating and drinking, pain and unpleasant cutting sensations are felt.
Areas with a favorable environment for development are affected - carious cavities, tartar, in children - the place where the wisdom tooth is cut. At risk are people suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, blood.
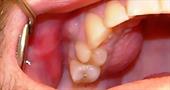
With an average degree , 1-2 days after the reddening of the gums, it covers with a gray-white coating, then ulcers appear. They consist of structureless tissue containing many microbes. When removing the top layer, the mucosa bleeds. Stomatitis first captures small areas, gradually growing around all the teeth.
A severe degree is characterized by a sharp increase or decrease in temperature (35-39 degrees), severe headache, nausea. Ulcers are deep, any touch to the lips and oral cavity causes unbearable pain.
The inflammatory process spreads throughout the oral mucosa - tongue, sublingual part, palate, inner surface of the cheeks and lips.
Secondary symptoms include an increase in lymph nodes, increased salivation (2.5-3 l / day). Saliva becomes thick and viscous, acquires a red tint due to bleeding gums. The smell from the oral cavity is sharp, rotting. Due to dead cells, the gum tissue is deformed. Appetite disappears, lethargy and drowsiness appear. Depending on the body's resistance, there is an increase in temperature up to 38 degrees.
The acute period lasts for 12-15 days, with high-quality treatment, this period is reduced to 4-5 days. Recovery of the affected epithelium begins from the edge of the ulcer. Gradually, the mucosa is cleared, salivation returns to normal.
The disease requires immediate treatment. The necrotic process on soft tissues, if therapy is ignored, penetrates to the bone base of the jaw and causes serious complications - osteomyelitis, inflammation of the middle ear, rhinitis, tooth loss, endocarditis.
If quality treatment is not carried out in time, ulcerative stomatitis flows into a chronic form.
Diagnostics
Ulcerative stomatitis has a characteristic symptomatology that cannot be confused with another disease. On a visual examination, the specialist assesses the condition of the oral cavity - the condition of the mucous membrane, the nature of the ulcers, the severity.
A number of analyzes are being carried out:
- Cytological;
- microbiological;
- Biochemical and clinical (blood);
- PCR study of scrapings.
Ulcerative stomatitis occurs against the background or due to other problems in the body, so the patient receives a referral to an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, allergist.
Vincennes stomatitis is more difficult to recognize due to similar symptoms with blood diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must undergo a series of laboratory tests.
Analyzes:
- HIV;
- pathohistological;
- Bacterioscopic;
- Cytological;
- Wasserman reaction;
- General blood analysis;
- Urine.
To prescribe high-quality therapy, the doctor finds out the level of sugar in the blood, the state of the immune system.
Treatment
The method of treatment of ulcerative stomatitis depends on the physical condition of the patient, the results of tests and the severity of the disease.
In dental practice, phased treatment is used:
1. Local therapy.
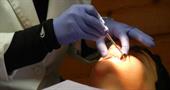
At the first stage, the doctor performs a professional cleaning of the oral cavity - removes tartar and plaque, seals carious cavities. After that, irrigation is carried out with solutions (potassium permanganate, furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide) under pressure with a special syringe. Particular attention is paid to the interdental areas, where the greatest number of pathogenic microbes accumulates.
With a mild form, a simple rinsing of the oral cavity with infusions of medicinal herbs is used.
In severe form, necrotic tissue is removed surgically under local anesthesia. For quick healing of wounds, ointments and oils with a regenerating effect are used (Solcoseryl, Metrogyl Denta, peach oil).
2. General therapy.
Antibiotics are used to clear the infection. A visible improvement occurs in 2-3 days - the mucous membrane is cleared, the putrid smell disappears, bleeding gums disappear.
For the correct choice of the drug, additional research is necessary.
In general therapy, antihistamines and antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
3. Therapy of concomitant diseases.
In parallel with the main treatment, the treatment of diseases that caused ulcerative stomatitis is carried out.
4. Therapy with immunomodulators.
To eliminate vitamin deficiency and increase overall immunity, the patient is prescribed a course of multivitamins or a vitamin-mineral complex. At this stage, it is possible to use traditional medicine recipes - take a rosehip decoction, echinacea tincture inside.
Timely seeking medical help allows you to get rid of the problem in 6-8 days without serious consequences. If ulcerative stomatitis has flowed into a chronic form, it will take more time (several weeks). Treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Preventive measures include simple recommendations - daily oral hygiene, preventive dental check-ups twice a year, proper nutrition.