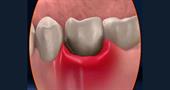
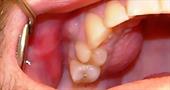
Apical periodontitis is one of the most common dental diseases of all types of periodontitis. Apical periodontitis can be acute or chronic and infectious or non-infectious.
Apical periodontitis can be judged by the characteristic inflammatory process near the top of the tooth root.
Causes and symptoms
The main causes of this disease include:
- getting an infection, such as staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus, etc.;
- mechanical damage or trauma to the tooth: root fracture, dislocation, damage by instruments during treatment;
- medicinal and chemical substances.
Symptoms of apical periodontitis:
- sharp pain occurs either after touching the diseased tooth, or in the evening;
- the pain is throbbing, constant, may increase over time;
- pain spreads to the ear, weight, eye;
- palpable swelling of the soft tissues of the face;
- swelling of the gums;
- enlargement and soreness of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- slight increase in temperature (37–37.5 °С);
- weakness and dehydration of the body;
- headache.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Diagnosis of periodontitis in the early stages plays a big role. The earlier the problem is found, the faster and easier the treatment will be. Diagnosis of apical periodontitis is different in children and adults.
Diagnosis of children's periodontitis consists in the obligatory passage of an x-ray of a problematic temporary tooth or inflamed gums. With the help of the resulting image, the dentist will be able to accurately determine the extent to which the problem has spread to the rudiment of the permanent tooth and prescribe a treatment that will not harm its further development.
Diagnosis of periodontitis in an adult consists of questioning the patient and examination. In this case, attention is paid to the following factors:
- collection of complaints from the patient, the nature of pain;
- examination of the problem area of the oral cavity;
- assessment of the severity of inflammation;
- analysis and comparison of symptoms with other similar diseases and the establishment of an accurate diagnosis and severity of the disease.
Treatment
Therapeutic treatment of acute periodontitis begins with the introduction of anesthesia to relieve pain and open the diseased tooth. The next step is to clean the tooth surface from carious tissues and inflamed pulp. After the entire accessible surface of the diseased tooth is cleaned, they begin to clean the canals so that the infiltrate and exudate can freely exit - this is the basis of treatment.
Since all the procedures described are quite painful, they are necessarily performed under anesthesia, and for a complete recovery, a course of antibiotic treatment is prescribed. Also, the dentist will advise which painkillers are best taken for toothache after the anesthesia has expired. In addition to the prescribed course of antibiotics, it will be necessary to rinse the mouth so that the inflammation passes faster and the toothache no longer disturbs. After apical periodontitis is cured, a special crown can be applied to the damaged tooth.
Surgical treatment of acute superficial periodontitis is carried out if the inflammation has damaged the bone tissue. This usually happens when you belatedly seek help from a dentist. If the root of the tooth has been completely damaged and collapsed, then the tooth is amputated. If the surface of the root of the tooth is damaged, a resection is performed.
If the treatment goes without complications, it is carried out in three stages until complete recovery. The next visits to the dentist will be for cosmetic measures to restore the function of the tooth or its prosthetics.
There are contraindications to treatment for acute superficial periodontitis:
- pronounced sepsis;
- no change for the better after a day of antibiotic treatment;
- tooth mobility of the third degree;
- a deep gingival pocket reaching the border of the apical zone of the root.
Extreme and quick measures must be taken with a strong increase in the inflammatory process of facial tissues. In this case, the periosteum should be dissected, drained, and in extreme cases, the tooth should be removed.
Prevention of periodontitis
Preventive measures to prevent periodontitis include:
- Compliance with oral hygiene: you should brush your teeth regularly, choose the right toothbrush and paste, use dental floss if necessary.
- Visits to the dentist: it is necessary to visit the dental office for prevention at least 2 times a year. At the first symptoms of toothache, inflammation of the gums or the appearance of caries, seek specialized help.
- Healthy nutrition: the health and strength of teeth depend on the content of vitamins and minerals that enter the human body with food.
- Controlling bad habits such as chewing on pencils and pens, cracking nuts with your teeth, etc.