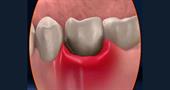
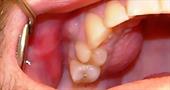
Aphthous stomatitis is a common dental disease, accompanied by the presence of ulcers on the oral mucosa. Aphthae are ulcers located separately or in a group on the oral mucosa. The approximate size is 5 mm. The formation of erosion in adults is accompanied by painful sensations.
Causes
According to studies, the main reason for the appearance of aphthous stomatitis is a decrease in the protective functions of general immunity. The oral mucosa is the strongest of the entire body. The main mass of pathogenic microorganisms enters through the mouth, so it has a high level of resistance.
Against the background of weakening the protection of general immunity, local resistance to viral diseases also decreases. During such a period, the number of "harmful" bacteria increases several times.
Secondary causes of aphthous stomatitis in adults:
- Past illnesses - occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, herpes, measles.
- Oral injuries are injuries caused by sharp edges of fillings, burns from hot food, scratches from chipped teeth and hard foods.
According to statistics, 40% of patients who have had aphthous stomatitis claim that dental problems began from the moment of traumatic damage to the oral cavity.
- Allergic reaction.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Heredity - the risk of the disease increases if one or both parents suffered from various forms of stomatitis.
- Hormonal failure or restructuring is relevant for women during pregnancy, lactation, menopause and menopause.
- Improper nutrition or beriberi - a lack of vitamins A, C and group B, zinc, folic acid, selenium and iron in the body contributes to the formation of aphthae.
- Dental diseases - caries, periodontitis, tartar , inflammation of the pulp.
- Nervous exhaustion - stress and strong feelings reduce general immunity, while the local resistance to pathogenic viruses decreases.
Aphthous stomatitis tends to return to patients whose immunity is not able to recognize dangerous microorganisms. This genetic feature cannot be influenced in any way.
Stages and symptoms
The disease at each stage of development in adults has its own symptoms and clinical manifestations.
In the prodromal period, the symptoms are similar to SARS - the body temperature rises to 37.5-39 degrees, the head starts to hurt, sweating increases. The patient feels chills, apathy and fatigue. With pressure in the back of the head, neck and jaw, enlarged lymph nodes are determined.
In the oral cavity, dryness of the mucous membrane is observed, some areas turn red and begin to become inflamed. Eating becomes uncomfortable - when chewing, pain is felt.
At the aphthous stage, aphthae are formed - round or oval sores with a small red border around the edge. A gray fibrinous plaque forms in the center. The place of appearance is the inner part of the cheeks and lips, the sky, the tonsils. When touched, the patient feels discomfort. The general condition worsens, appetite decreases - it hurts to swallow and chew. In the blood, the number of leukocytes sharply decreases.
The healing stage occurs in 7-10 days. The film covering the ulcers is removed on its own 2 days after the completion of the acute stage. The aphthae are tightened, reddened areas of the mucous membrane appear in their place. After complete healing (it will take another 3-4 days), no traces remain in the oral cavity and on the lips. Eating and drinking no longer causes discomfort.
Forms of aphthous stomatitis
The nature of the formation of aphthae and lesions on the oral mucosa is different, and depends on the form of stomatitis:
- Fibrous - the symptoms are similar to the clinical manifestation of herpetic stomatitis: itching, burning, fever, ulceration, healing after 12-14 days. Their main difference is that aphthae in herpetic stomatitis are located outside on the lips, and in aphthous stomatitis - inside the oral cavity;
- Necrotic - occurs against the background of severe somatic diseases. At contact, the ulcers are very painful, the acute period is delayed for 3-4 weeks;
- Grandular - the development of the disease is associated with disruption of the ducts of the salivary glands. Aphthae are formed at the site of the glands, healing occurs in 17-20 days;
- Scarring - occurs against the background of incorrect therapy of the granular form of stomatitis. After a while, the ulcers increase in size (up to 1.5 cm). They are located locally on the ducts of the glands, the sky. The healing stage is long - 2.5-3 months;
- Deforming - a severe form, accompanied by changes in the connective tissues of the palate, the inner side of the lips.
For successful treatment, it is necessary at the initial stage to correctly determine the stage of aphthous stomatitis, the cause of its occurrence.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out at the dentist's office. During a visual examination, the following are determined: the stage of stomatitis, lesions of the mucous membrane, the method of treatment. The patient is asked a number of questions - how long ago the inflammation began, is there an increase in temperature, etc. On examination, the doctor looks at the structure of aphthae, which are in an acute phase and do not heal within 12-15 days. This may be a sign of cancer. For the accuracy of the diagnosis, tests are prescribed - blood, biopsy, bacterial culture. After receiving the results, treatment is prescribed.
Aphthous stomatitis has 2 forms - acute and chronic.
- The appearance of an acute form is associated, in most cases, with a viral infection that has been previously transferred. Pathogenic infections (staphylococci, streptococci) are found in the blood and epithelium.
- The chronic form is characterized by a period of relapse and remission over several years. The cause is the patient's chronic diseases, mucosal injuries. With a relapse, there are no acute symptoms - there is an increase in temperature. There is slight swelling in the oral cavity, the number of aphthae is insignificant. Remission occurs in 8-10 days.
Treatment
Therapy of aphthous stomatitis takes place at home using a conservative method. The impact includes local and general treatment.
The main cause of the disease is a decrease in general immunity, therefore, at the initial stage of general treatment, immunomodulators are prescribed - Immunal, Amexin and a course of a vitamin-mineral complex (necessarily includes folic acid, riboflavin, vitamins C and group B).
Interferon and Decamine are used as anti-inflammatory agents.
To avoid the manifestation of allergies, antihistamines are taken - Tavegil, Fenkarol.
Local treatment is aimed at relieving the main symptoms of the disease - swelling, discomfort and pain during eating and talking, violation of the microflora of the oral cavity. For quick and effective treatment, the doctor prescribes drugs of different directions of action:
- Antiseptics - solutions of potassium permanganate, Chlorhexedine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide (each separately). Rinsing allows you to clean the mucous from plaque and pathogenic bacteria. Sprays are used as a disinfectant: Geksoral and Lugol;
- Painkillers - in the acute stage, appetite disappears due to the painful contact of food and ulcers. For the period of treatment, before each meal, the cavity is irrigated with Anestezin, Trasilol or Lidochlor;
- Wound healing - at the stage of local treatment, it is important to get rid of aphthae as soon as possible to improve the general condition of the patient. The doctor prescribes Vinilin, Actovegin-gel or Solcoseryl.
To increase reactions in the body, Pyrogenal, Lysozyme are additionally taken.
It is recommended to use an aqueous solution with sodium thiosulfate daily to cleanse the body.
Therapy for acute and chronic forms is the same. For the period of relapse, the oral cavity is treated locally with antibacterial agents - Oracept, Tantum Verde.
At the time of treatment of any form of stomatitis, it is worth adhering to a strict diet - do not eat solid, salty, sour foods, exclude allergenic foods. The menu includes lean cream soups, liquid cereals, steamed vegetables. Recommended drinks are unsweetened strained compote, tea without sugar, plain still water.
ethnoscience
Recipes for a home first aid kit cannot completely get rid of aphthous stomatitis, but it is possible to significantly alleviate the patient's condition.
- Natural immunomodulators are alcohol tinctures of eleutherococcus, propolis, echinacea and ginseng.
- Wound healing properties have peach and sea buckthorn oil.
- For a disinfecting effect, infusions are used for daily rinsing on medicinal herbs - chamomile, calendula, sage. A solution based on soda and salt helps to clean the oral cavity.
- To reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria in the mouth, it is recommended to chew a freshly cut aloe leaf (thorns are removed).
Prevention
Aphthous stomatitis is accompanied by painful symptoms and a lot of discomfort. For the health of the oral mucosa and lips, you should not abandon preventive measures:
- Once every six months it is necessary to visit the dentist for a preventive examination and removal of tartar.
- Pick up a toothbrush and paste, taking into account individual characteristics.
- Nutrition should be balanced, with enough vitamins and minerals.
- Go in for sports and give up bad habits.
- In the event of any illness, immediately seek qualified help.
Preventive measures are advisory in nature and do not constitute a guarantee.