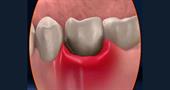
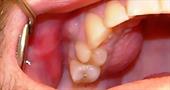
A tooth abscess is an infection caused by bacteria. An abscess may or may not be painful, but in any case it is characterized by the presence of pus. This type of infection usually occurs at the root of the tooth or at the level of the gums around the tooth.
An abscess can develop if there is a mechanical injury to the tooth (a chipped or broken tooth), if the tooth is affected by caries, which has already grown and reached the central cavity of the tooth. In some cases, the infection occurs due to gum disease, such as periodontitis. If a tooth abscess is left untreated, the infection can gradually reach the jaw and lead to serious complications.
Abscess due to a diseased tooth
It is important to note that caries and abscess can develop without causing pain to a person. But if the infection occurs quickly, swelling occurs, accompanied by severe pain. In this case, you should immediately go to the dentist, who will conduct an x-ray examination and make an accurate diagnosis.
Abscess due to diseased gums
If you do not follow oral hygiene and do not remove plaque in a timely manner, it will accumulate and eventually turn into tartar , which will be deposited on the teeth and gums. Tartar can cause inflammation and subsequent infection of the gums.
If tartar is not removed by brushing, it will gradually move through the gums and begin to break down the bone that holds the teeth. This condition is called periodontitis, a disease that can generate an abscess at the gum level with swelling and pain. But periodontitis can develop very slowly, without pain, but destroying the bones. The tooth begins to loosen more and more in the gum until it falls out on its own or is removed surgically.
Symptoms
The main symptom of an abscess is a sharp pain in the affected tooth. Sometimes the disease proceeds with fairly long periods without pain (from several days to several months), so the person may not know that he has an abscess. Symptoms may also include:
- Redness and swelling of the gums;
- Pain when chewing;
- Headache, fever and general malaise;
- The presence of pus (green and unpleasant odor). After it flows out, the pain immediately stops.
Complications
If left untreated, a dental abscess can lead to serious health complications, even death.
- Fistula . When a tooth abscess becomes chronic, an open wound oozing pus into the oral cavity appears. When a fistula appears, the pain usually subsides and a white or red button-like spot can be seen on the gum.
- Loss of a tooth. An abscess infects the bones that support the tooth. If the damage is severe, such as from periodontal disease, the tooth begins to loosen and eventually falls out.
- brain abscess. The infection can be transmitted from the teeth to the brain through the blood vessels. Brain infection is a direct path to coma.
- Sinusitis. The roots of the teeth (their upper ends) are located near the mucous membranes of the nose. If a tooth abscess is accompanied by pus, it can fill the sinuses and cause sinusitis.
- Bacterial endocarditis . Occurs when bacteria from a tooth abscess reach the heart through the blood vessels. As a result, blood poisoning occurs, leading to fatal consequences.
- Angina Ludwig. This is a serious infection, sometimes fatal, that affects parts of the face and lower jaw. It usually occurs in adult patients suffering from a dental abscess that has not been treated. The danger lies in the fact that inflammation of the soft tissues of the mouth can grow and block the airways. The result is suffocation and death.
Treatment
Treatment of an abscess depends on its origin (tooth or gums), location and includes:
- Taking antibiotics. However, treatment is not limited to antibiotics alone, as they are most effective at the start of therapy and can only temporarily reduce the abscess;
- Drainage of pus if the inflammation is very severe;
- If the abscess is due to diseased gums, drainage and curettage may be required;
- If an abscess has developed as a result of a diseased tooth, a root canal cleaning will be required, followed by the installation of a crown;
- If someone does not have the financial means to install a crown, the presence of an abscess in the oral cavity cannot be allowed, that is, the tooth must be removed. Then it will be possible to insert the implant (when the opportunity arises). Implants are not as good as "native" teeth, but still a good alternative;
- If the tooth is severely decayed or does not have enough bone to hold on, extraction is the only option.
Prevention
A tooth abscess is an unpleasant and painful phenomenon that can be avoided if you follow simple rules:
- Regular brushing of teeth and oral cavity (brush your teeth three times a day and rinse twice);
- Visit the dentist regularly, preferably twice a year;
- Conduct regular cleanings at the dentist and timely remove tartar and deposits;
- Cut down on smoking or quit altogether.