Prolonged inflammation of the gums requires treatment and preventive care. Left unattended, the disease in most cases leads to the destruction of the tissues surrounding and holding the tooth in the jaw, which, in turn, is fraught with loss of teeth.
Swelling of the gums, their bleeding during cleaning are quite common: according to statistics, from 30 to 70% of children and more than 70% of adults are affected by the disease. However, these symptoms are not accompanied by severe pain, and the person is in no hurry to see a doctor. And in vain, because "silent" gingivitis can progress into destructive forms of periodontal disease and deprive you not only of a beautiful healthy smile, but also of the teeth themselves. In some cases, gingivitis can be a symptom of other serious human conditions, such as diabetes.
That is why it is so important to identify the causes and eliminate this disease in time. You can detect gingivitis during a preventive examination, when the doctor can give recommendations on care and prevention, as well as prescribe the necessary treatment. At this stage, periodontal disease is easily treated, but neglecting the problem for a long time can lead to irreversible changes that require surgical intervention.
How does gingivitis appear?
The most common cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of bacterial plaque on the teeth due to poor oral hygiene. The second reason is orthodontic pathologies and errors in orthodontic treatment, which, in combination with the first reason, contribute to the intensive development of undesirable microflora in the mouth. The most common culprits for inflammation are bacteria such as Streptococcus oralis, Bacteroides gingivalis, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Actinomycetes comitans, Prevotella intermedia, Actinomyces israelii, less commonly viruses and fungus. Biofilms formed from these microorganisms form plaque on the surface of the teeth, causing redness, swelling and bleeding.
A number of factors can contribute to the development of gingivitis, they can be conditionally divided into two groups:
1. Social (behavioral) factors:
- smoking;
- poor oral care;
- lack of solid food in the diet, malnutrition;
- childhood;
- a state of prolonged stress.
2. Medical factors:
- unsatisfactory caries treatment and fissure filling;
- bite pathology;
- dental deposits;
- violation of nasal breathing, breathing through the mouth;
- weakening of the immune system;
- the patient has diabetes;
- pregnancy;
- beriberi (primarily a lack of vitamin C);
- colds and viral diseases;
- toxic poisoning of the body with heavy metals.
Also, gingivitis can develop against the background of long-term use of certain types of oral contraceptives.
Manifestations and varieties of gingivitis
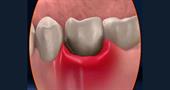
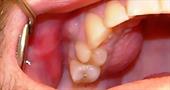
You may have noticed blood on your toothbrush, swollen gums; if the gums are reddened, discomfort is felt while eating, it can be assumed that this is the result of the development of gingivitis.
This disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- discomfort, tension in the gums, swelling;
- gum line disorders;
- change in the color of the gum tissues to purple-bluish;
- bad breath;
- itching, burning;
- bleeding (in some cases);
- the appearance of gum pockets;
- plaque on the surface of the teeth and surrounding tissues;
- hypersensitivity while eating.
Often these signs are amplified against the background of beriberi in the spring and autumn periods.
Gingivitis is distinguished by the nature of the course (acute and chronic) and by the type of manifestation of the pathology (desquamative, hyperplastic, ulcerative, atrophic and acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis).
Methods for the treatment of gingivitis
If you notice one or more of the above symptoms in yourself, without wasting time on self-treatment, hurry up to see a dentist. Wrong "self-prescribed" recipes can not only not help, but also intensify the course of the disease.
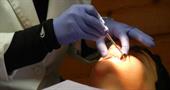
The doctor will prescribe treatment depending on the nature and degree of tissue damage: it can be professional cleaning with the removal of deposits, treatment with specialized solutions, the appointment of specialized gels and ointments applicable at home; you may need antibiotic therapy, including antibiotics; in some cases, it will be necessary to resort to a surgical method of treatment.
Your dentist may also recommend a course of orthodontic treatment. Since gingivitis often indicates a general decrease in the body's immunity, the use of drugs that affect the body's immune properties may be prescribed. These medicines help maintain the protective properties of the oral cavity.
In addition to therapy, you will receive care recommendations and information about modern daily care products: today there are many technical innovations and specialized pastes on the market that can significantly increase the effectiveness of oral cleansing and ensure a high level of hygiene at home. Electric and ultrasonic toothbrushes, irrigators and dental centers make high-performance care more affordable.
As a rule, gingivitis is successfully treated, since the tissues are able to recover, and the periodontal bonds are not yet broken.
Gingivitis Prevention
As noted above, gingivitis is most often the result of insufficient oral hygiene, therefore, its occurrence can be prevented by observing simple rules:
- brush your teeth regularly, at least 2 times a day;
- do not forget to pay attention to the tongue: this is a favorite place for bacteria when brushing your teeth is often ignored;
- use a suitable toothbrush and floss; if possible, use technical care products (special brushes and irrigators);
- visit the dentist for preventive examination at least 2 times a year;
- seek the help of a hygienist (specialist in professional teeth cleaning) at least once a year.